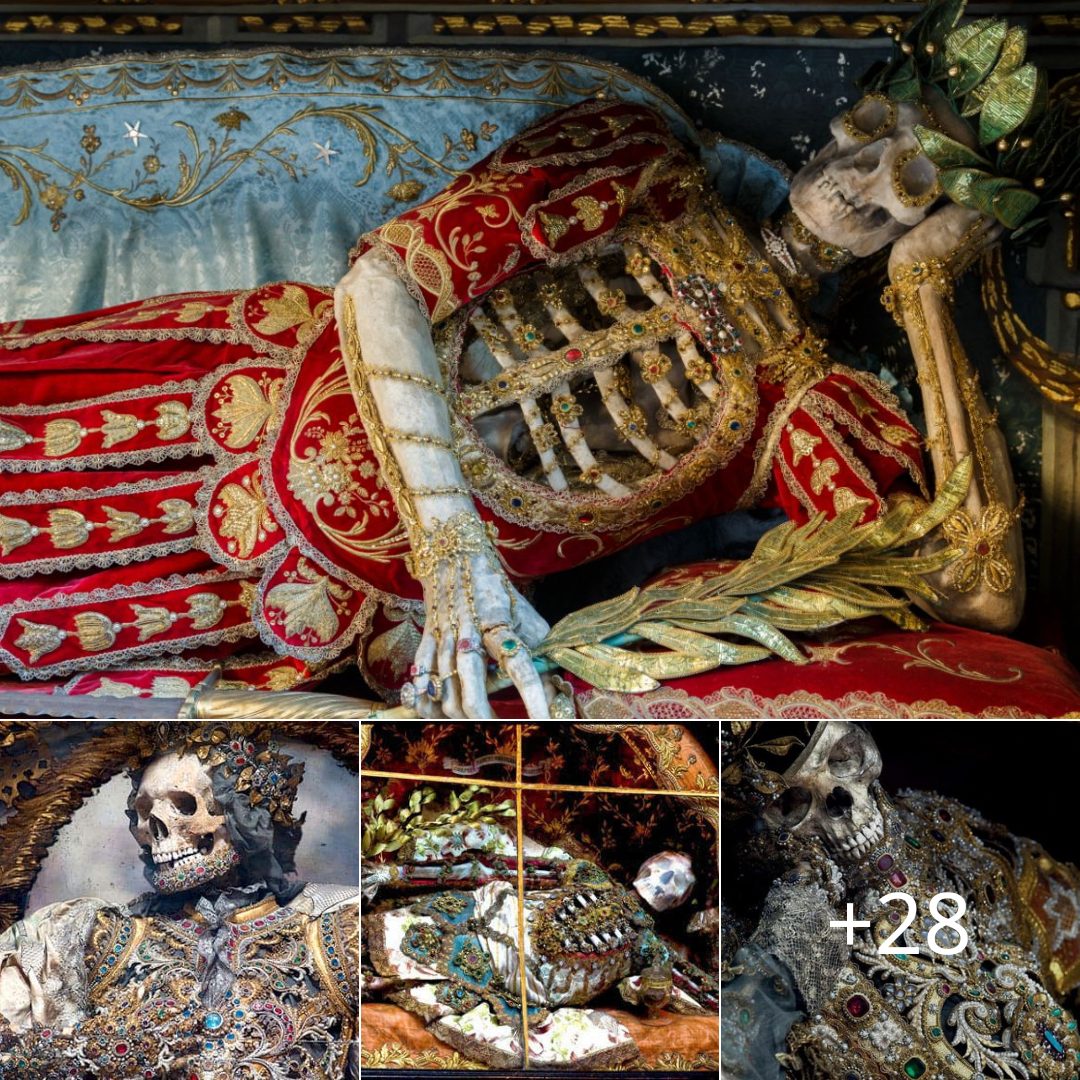
Archaeologists in Mexico have unearthed a remarkable burial in the ancient ruins of Teotihuacan containing a 1,600-year-old skeleton of an upper-class woman with an elongated skull, stone encrusted teeth and a prosthetic tooth made of a green stone known as serpentine. She was buried with 19 jars of offerings.
Agence France-Press reported that the skeleton has been named “The Woman of Tlailotlacan” after the neighbourhood where it was found, just near Mexico’s famous ruins of Teotihuacan, which is located about 30 miles (50 km) northeast of Mexico City. Dating back around 2,500 years, Teotihuacan is one of the largest and most important sacred cities of ancient Mesoamerica, whose name means “the city of the gods” in the Nahuatl language of the Aztecs. It once supported an estimated population of 100,000 – 200,000 people, who raised giant monuments such as the Temple of Quetzalcoatl and the Pyramids of the Sun and the Moon. However, much about Teotihuacan remains unknown, including the origin and language of the people who lived there, as they did not leave behind any written records.

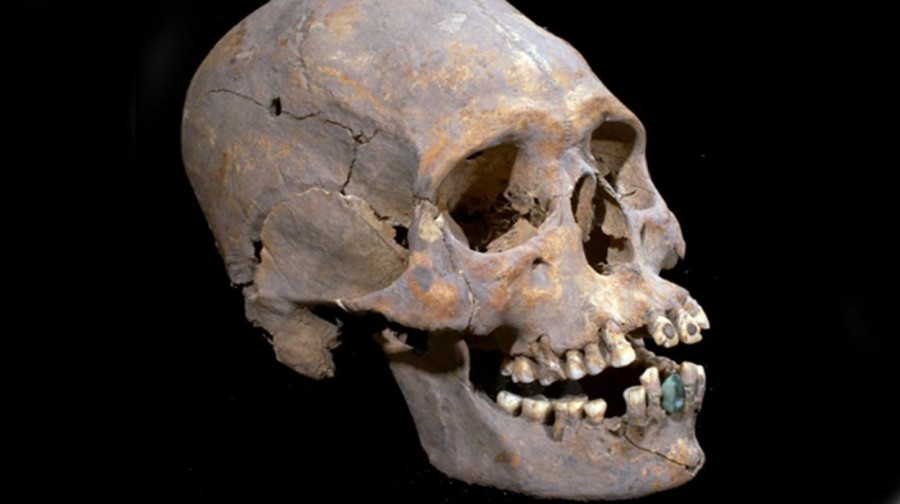
The National Anthropology and History Institute (INAH) said the woman, who was between 35 and 40 years old when she died, was a foreigner to the area, as the way in which her skull had been deformed and her teeth encrusted with mineral stones was not usual for that region. The institute said in a statement that her cranium had been elongated by being compressed in a “very extreme” manner, a technique commonly used in the southern part of Mesoamerica, not the central region where she was found.
Her teeth contained two round pyrite stones, which were encrusted in her top front teeth. This was a practice that was used among the nobility in Maya regions in southern Mexico and Central America. The Maya are credited with being the masters of cosmetic dentistry as they were known to decorate teeth by embedding them with precious stones or by carving notches and grooves into them. Tiny holes were chipped out of teeth and ornamental stones—including jade—were attached with an adhesive made out of natural resins, such as plant sap, which was mixed with other chemicals and crushed bones. The dentists likely had a sophisticated knowledge of tooth anatomy because they knew how to drill into teeth without hitting the pulp inside.





