If the longest river in the world is the Nile River in Africa, then the largest river in the world is the Amazon River – this river has the largest basin and highest water flow in the world. At the same time, the largest tropical rainforest in the world is the Amazon rainforest, most of which is located in Brazil. The two are closely tied together to create the most diverse flora and fauna on the planet.
The Amazon rainforest is known as the “lungs of the Earth”, the air is quite fresh, there are also lush ancient forests and winding rivers, which look very beautiful and attract many people to come. This. It is home to the most species in the world, with more than 2.5 million species of insects and more than 10,000 species of plants and thousands of species of mammals, such as pythons, golden parrots, and freshwater dolphins. ..
But underneath these beautiful scenes and biodiversity, there are very scary dangers hidden.
What causes the Amazon River to be so terrible? And why don’t people dare swim in it?
Besides the fact that the Amazon is home to the giant Anaconda and countless other predators, one of the reasons comes from the name “Piranha”.
Assassin in the riverbed
The Amazon River is notorious for its terrifying and terrifying “Piranha fish” , which have many fangs and a crazy bite force, and can hunt in many groups. There are many opinions that they can eat a 450 kg cow in 70 seconds. All that remains is the skeleton.
Analyzing the infamous power of Piranha, Smithsonian Magazine (USA) said the factors that turn Piranha into a “nightmare” for many creatures in the riverbed:
1. Sharp teeth
Piranhas are known for their razor-sharp teeth and relentless bite. (The word piranha literally translates as “sawtooth fish” in the Tupí language of Brazil.) Real Piranhas have tricuspid teeth, with larger/longer incisors.
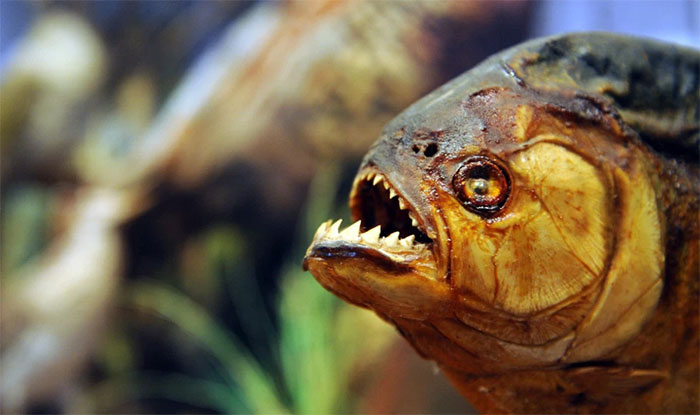

Piranha fish’s sharp teeth.
The shape of the Piranha’s teeth is often compared to the shape of a saw nose and this has clearly been adapted to their carnivorous diet. The actual tooth enamel structure of this fish is similar to that of a shark.
It is not uncommon for Piranha fish to change their teeth throughout their lives. However, while sharks replace their individual teeth, piranhas replace their teeth and jaws many times throughout their lifespan, which lasts up to 8 years in captivity. It is not uncommon for a Piranha to be missing half of its lower jaw.
There are many types of Piranha fish and they are both vegetarian and carnivorous. Their common foods include insects, fish, crustaceans, worms, animal carcasses, seeds and other plant materials.
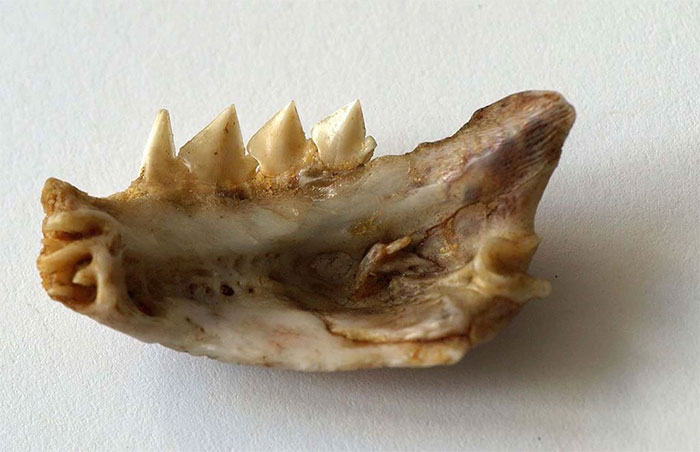

Jaw bone sample of Red-bellied Piranha (Pygocentrus nattereri). Wikimedia Commons/Sarefo
In a 2012 study in the journal Scientific Reports , researchers found that the black (or red-eyed) piranha (Serrasalmus rhombeus), the largest of the modern species, bites with maximum force. is 33 kg (3 times their body weight).
Using tooth fossil models, they discovered that the Piranha’s 10-million-year-old extinct ancestor, Megapiranha paranensis , had a bite force at the tip of its jaw as high as 484 kg. For reference, this species of Megapiranha paranensis weighed only 10 kg when alive, which means the bite force of Megapiranha paranensis is almost 50 times its body weight.
Science notes that the estimated bite force of the T.rex was three times higher than that of this ancient Piranha (Megapiranha paranensis) – but the “king of reptiles” was the T.rex. much heavier.
2. Apex hunting strategy
Not only possessing scary teeth, Piranha fish also possess a very clever prey attack strategy . A 1972 study of red-bellied piranhas found that this fish most frequently attacked goldfish in a laboratory setting, starting with the prey’s tail or eyes.
The researchers concluded that such an attack strategy would leave the piranha’s opponents immobilized or disoriented.
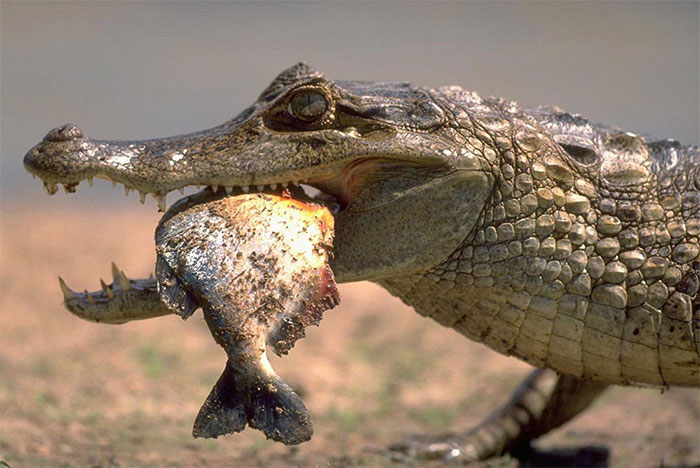

A scene of Caiman crocodiles eating fresh Piranha fish in Venezuela. (Photo: W. Perry Conway / CORBIS).
In addition, people can easily see Piranha fish often moving in groups. They do this for safety.
Piranha fish are not at the top of the food chain in the Amazon river bed. They are preyed upon by Caiman crocodiles, birds, river dolphins and other large Pescatarian fish. Therefore, traveling in groups in shallow flats has the effect of protecting the fish inside from attack.
3. Sensitive to noise and blood
A 2007 study linked noise, splashing water, and spilling food, fish or blood into the river with three cases of Piranhas attacking humans in Suriname (South American country).
As for blood, Piranha fish can smell a drop of blood in 200 liters of water. So, if you have even a minor wound, taking a dip in the Amazon River is not wise!
4. Piranhas only attack when they feel threatened
And although piranhas are famous for attacking people, there is not much evidence to support this. Like grizzly bears, wolves, sharks and pretty much any big scary thing with teeth, Piranhas will leave you alone if you leave them alone.
Black Piranha and Red-bellied Piranha are considered the most dangerous and aggressive species towards humans. However, veteran South American swimmers often emerge from piranha-infested waters without losing their flesh.
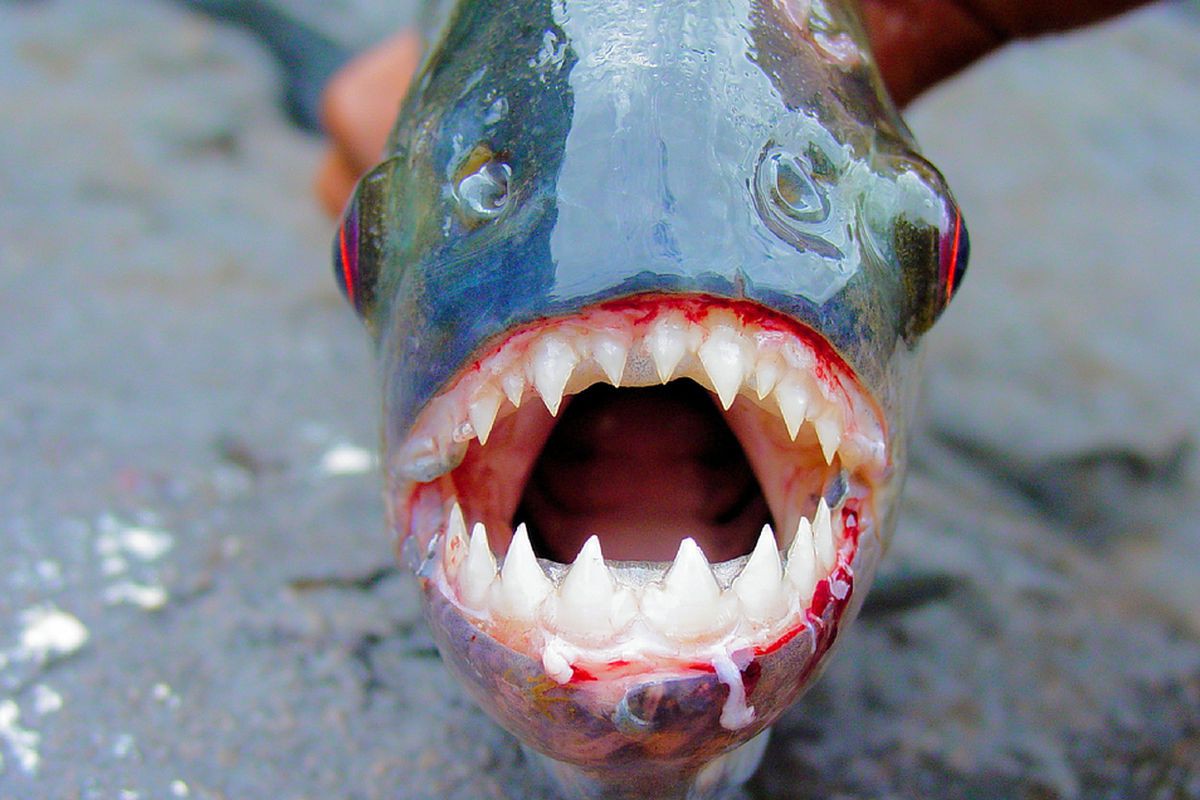

For normal people, danger occurs you move where the water level is low, prey is scarce (for Piranhas) or you disturb its breeding grounds at the bottom of the river – Basically, these are situations that Piranhas feel really threatened or when they are really hungry – therefore they will become more aggressive.
That’s why indigenous people rarely wade barefoot at the river’s edge. For them, hunting and eating Piranha fish is taboo, so they rarely touch this fish.
Scientists advise non-professionals not to go or swim in the Amazon River, avoid misleading them (being disturbed or potentially dangerous) so they attack humans.